Symptoms
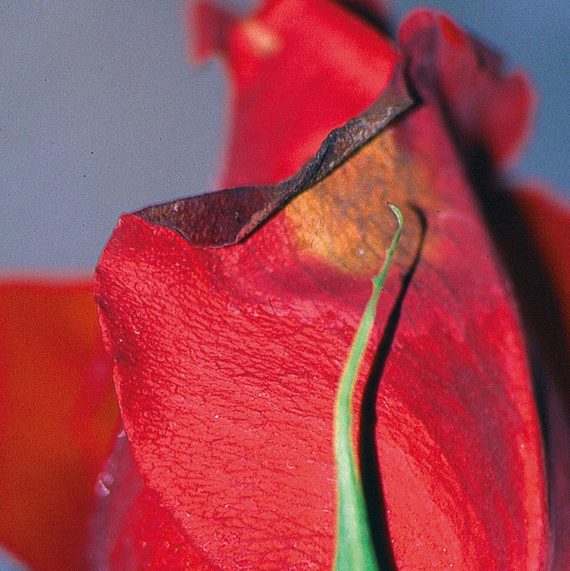
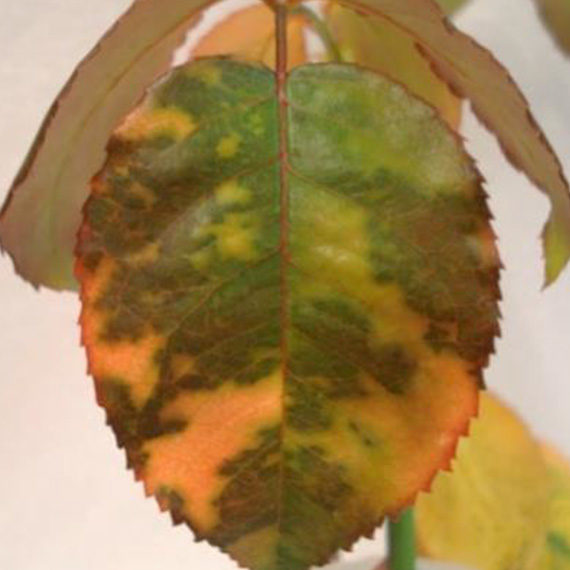
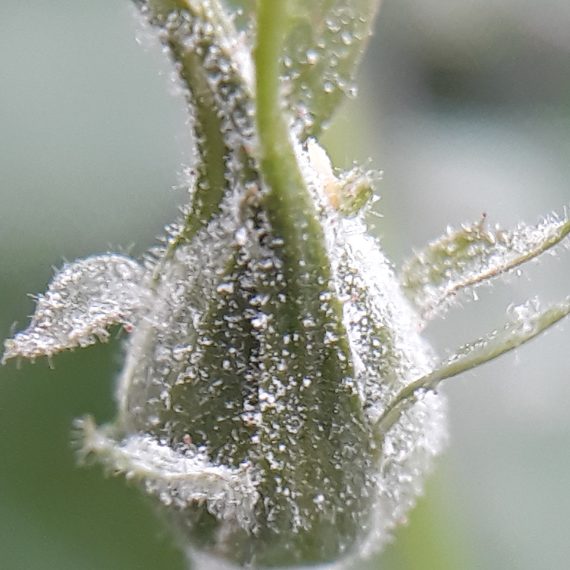
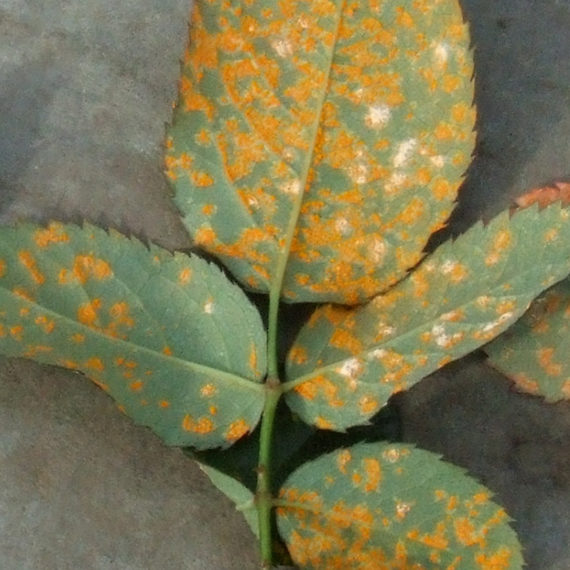
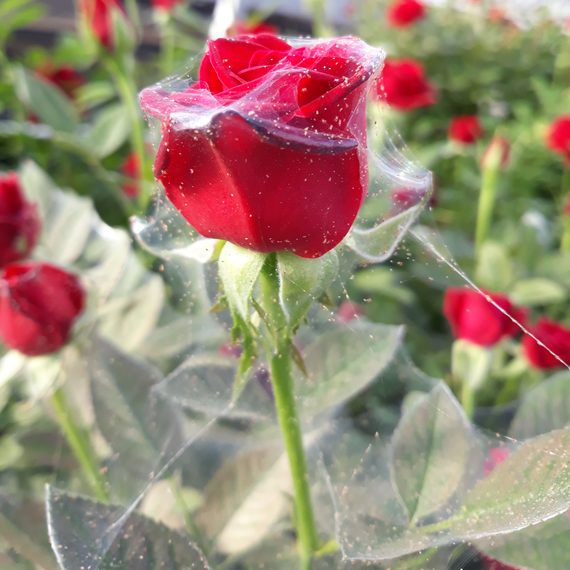
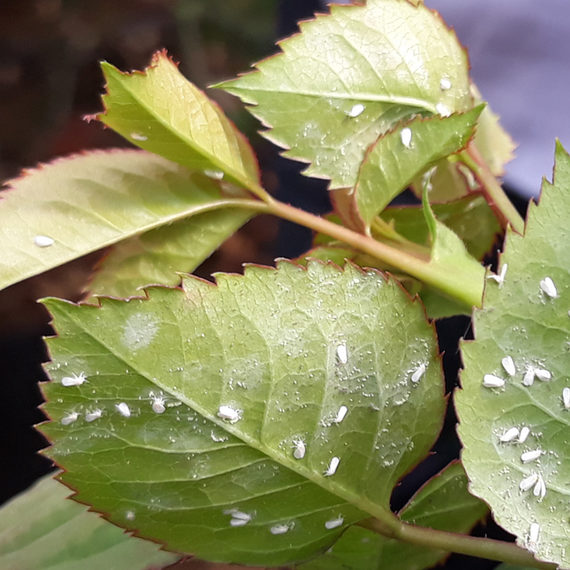
Adults are mainly flower-feeders but will also feed on stems and leaves of plants as well. Symptoms of damage may include: discolouration and scarring of open blooms, petals, deformation of buds and flower heads, as well as pimpling on some flowers as a result of eggs deposited beneath the tissue. After feeding on a plant, silvery necrotic spots will often appear which can affect the plants ability to photosynthesize, distort growth and further reduce the value of the plant. The wounds caused by thrips can pave the way for botrytis infection. Thrips have also been known to vector diseases to plants when feeding: most commonly Impatiens Necrotic Spot Virus (INSV).
Management
An Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programme involving greenhouse sanitation, insect-proof nets, yellow or blue sticky cards, biological controls and insecticide application.
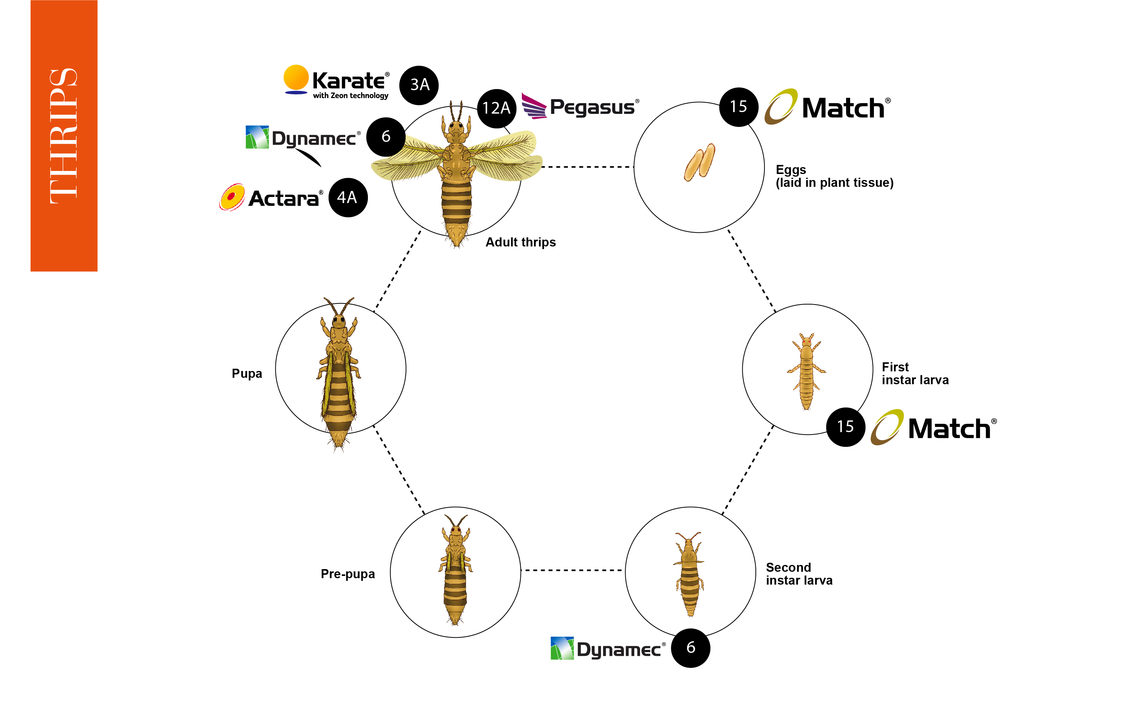
Thrips Life Cycle
Understanding a disease's life cycle is vital to maintaining control in your crops. Below is the thrips life cycle, to help you get the maximum control, the best products from our range have been incorporated.
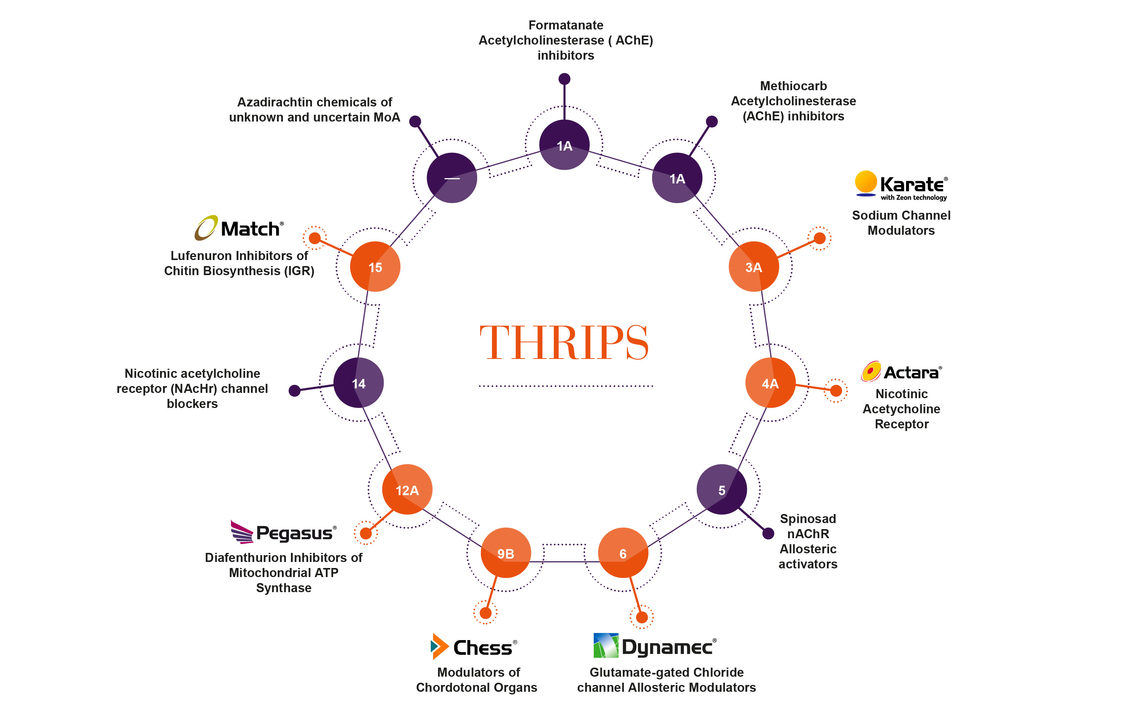
Managing Resistance
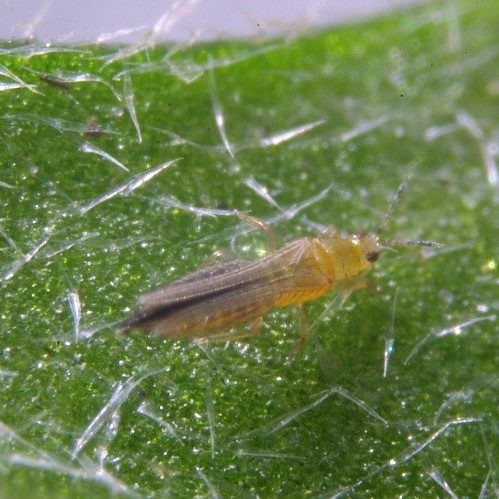
Thrips tabacii, Frankliniella occidentalis, Echinotrips americanus, Thrips setosus . These are some of the types of thrips with the most common in floriculture is the F. Occidentalis. This species is very polyphagous and causes damage in a wide range of crops as well as being a vector for virus. The development of thrips at 15⁰C is around +/- 44 days. When the temperature is higher, around 25⁰C, the cycle is halved to +/- 18 days so the short life cycle can mean the insect can become resistant very quickly. In a controlled environment it is good to start an integrated approach. When the infestation of thrips passes a threshold and damage is no longer tolerable, the use of a chemical control can reset the population. Alternating chemistry will help reduce resistance issues whilst ensuring that the available products remain effective.
To prevent a crop developing resistance it is important that you alternate between the different active ingredients. It is important to pay attention to the mode of action the product has. Rotation of products is a key strategy but it’s important those products have different IRAC codes, as this can reduce further resistance development. Ensure your program takes this into account. If you are in a situation where products with the same mode of action are applied twice in a row, moving to another product with a different IRAC group becomes more even more important.